5 Minute Overclock: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3050 to 2235 MHz

We’re overclocking the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3050 GPU up to 2235 MHz in 5 minutes or less using the EVGA Precision X1 software.
I’ll speedrun you through the OC settings and provide some notes and tips along the way. Please note that this is for entertainment purposes only and not the whole picture. Please don’t outright copy these settings and apply them to your system. If you want to learn how to overclock this system, please check out the longer SkatterBencher article.
All right, let’s do this.
5 Minute Speedrun
Open the EVGA Precision X1 software tool. This software tool provides us access to all the parameters exposed in the NVIDIA API. We want to adjust the parameters impacting the GPU Boost technology behavior.
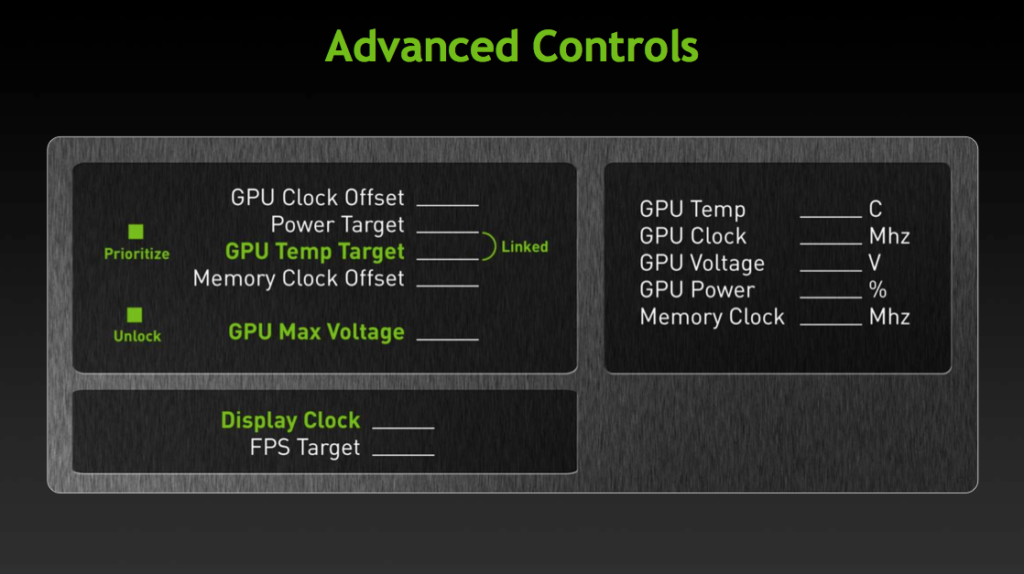
GPU Boost 4.0 is the frequency-boosting technology that’s embedded in all NVIDIA Ampere graphics cards.
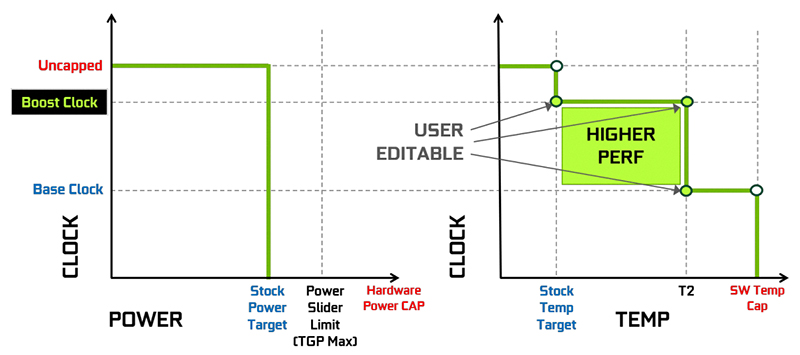
Set Power Target to 112%. This ensures the GPU Boost 4.0 algorithm will use the maximum available power consumption headroom.
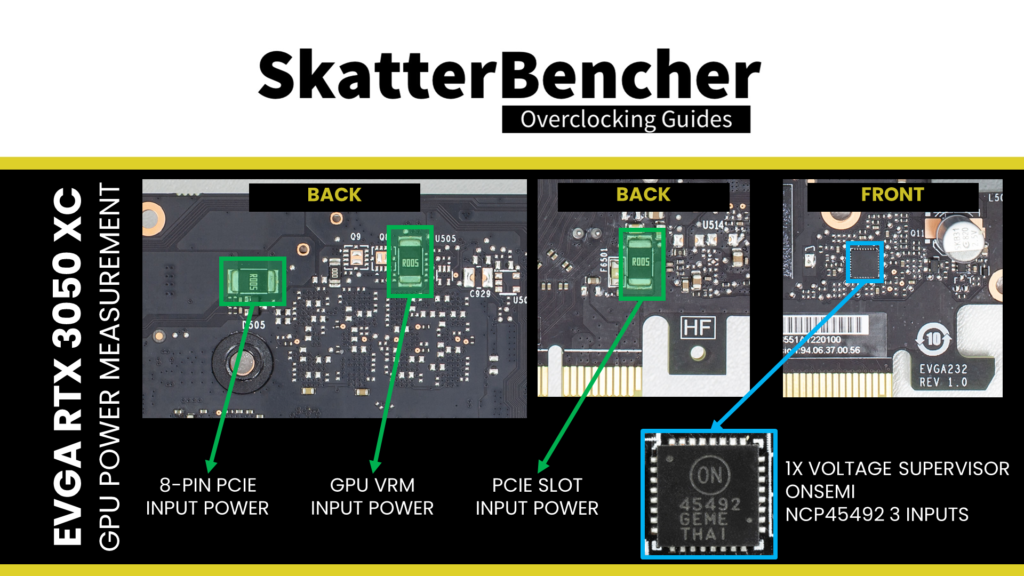
For the GeForce RTX 3050 GPU, that’s up to the Total Board Power of 145W, up from the default 130W. Note that just like on high-end graphics cards, the GPU monitors the power consumption using a voltage monitoring circuit on the PCB.
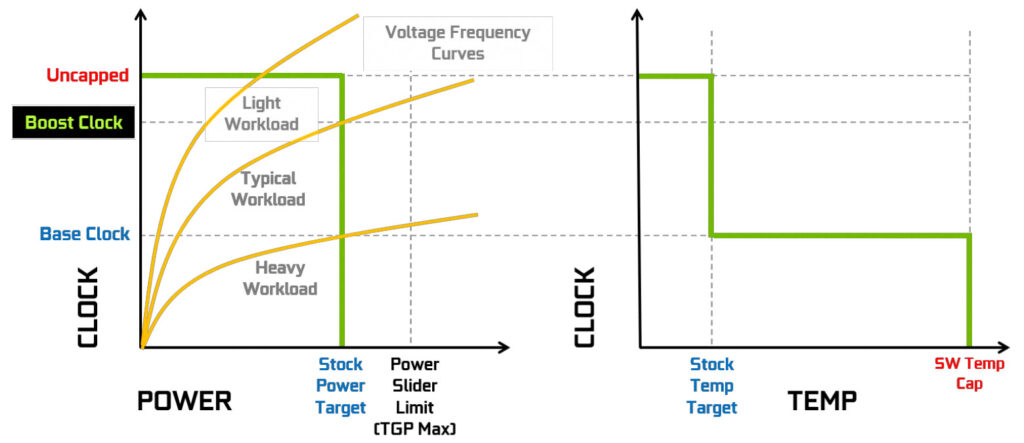
Set GPU Voltage to 100%. This enables the overvoltage feature present since GPU Boost 2.0. Overvoltage refers to the extended range between the reliability voltage (Vrel) and maximum overvoltage (Vmax) as specified by NVIDIA.
The reliability voltage, Vrel, is the highest voltage the GPU will safely run at without harming the long-term lifespan. The maximum overvoltage, Vmax, is the highest voltage NVIDIA will allow the GPU to run at, as it may hurt lifespan. This extended voltage range can be enabled or disabled by NVIDIA board partners in the graphics card VBIOS. If enabled, users like you and I can access the higher voltage by accepting the associated risks.
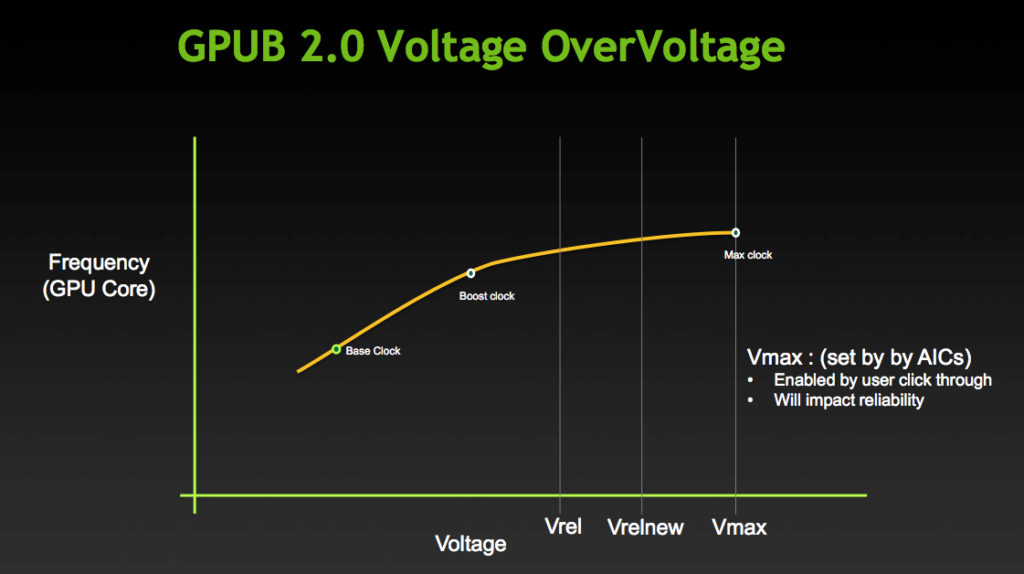
On this EVGA GeForce RTX 3050 XC GAMING graphics card, the reliability voltage is 1.081V, and the maximum voltage is 1.1V.
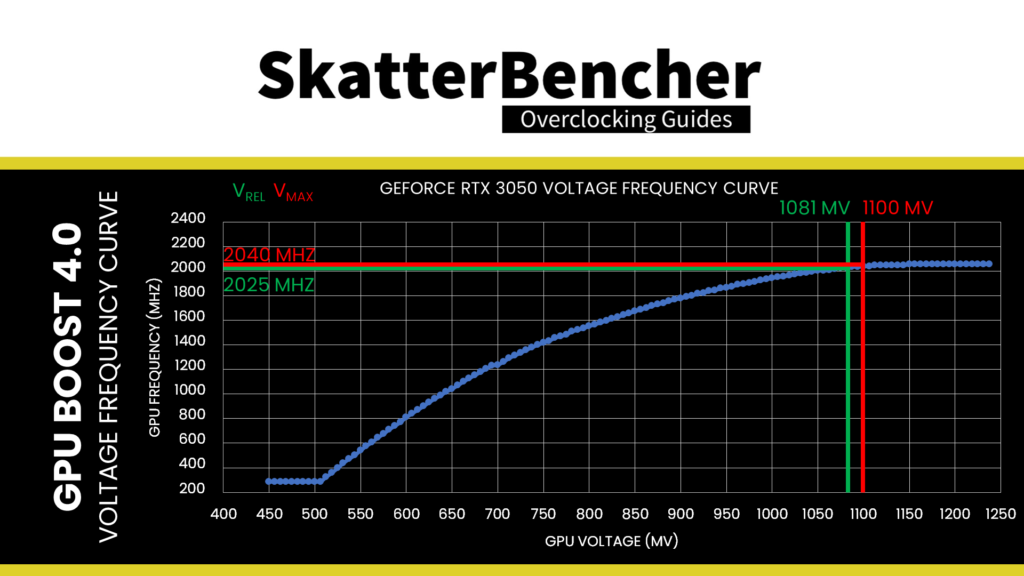
Set GPU Boost Clock to 2235 (+200). This offsets the entire GPU voltage-frequency curve by 200 MHz over the standard curve.
The voltage-frequency curve describes the relationship between a frequency and the voltage required to run that frequency. The NVIDIA Ampere GPU has 128 distinct, individually adjustable points on its voltage-frequency curve. On this RTX 3050, the V/F points range from 285 MHz at 450 mV to 2055 MHz at 1238 mV. If you have a lot of time, you can manually tweak each of the 128 points … but it’s a lot of work.
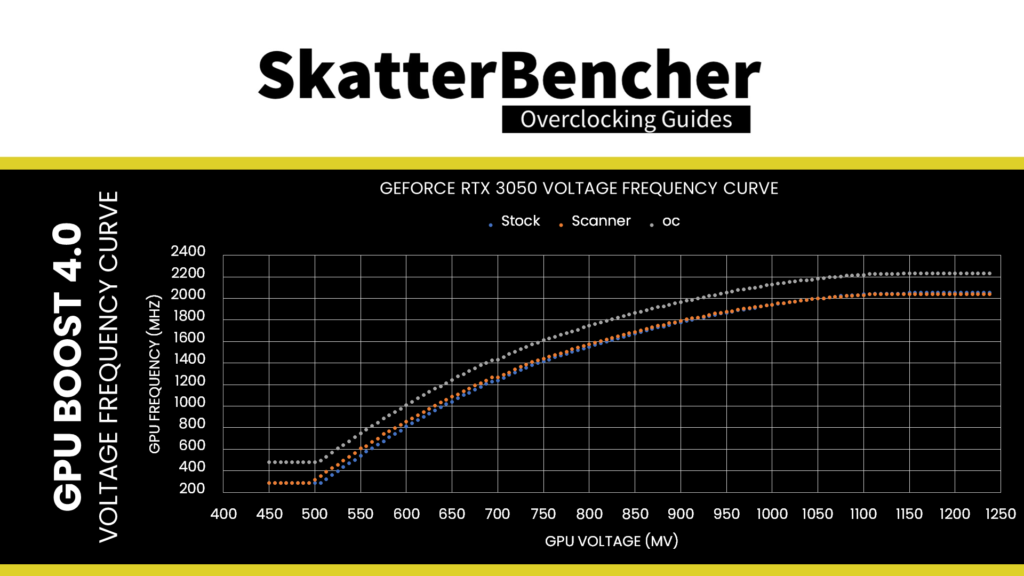
Set Memory Clock to 8301 (+1300). This increases the GDDR6 memory frequency from a default 1750 MHz to 2075 MHz.
GeForce RTX 3050 Overclock Performance Improvement
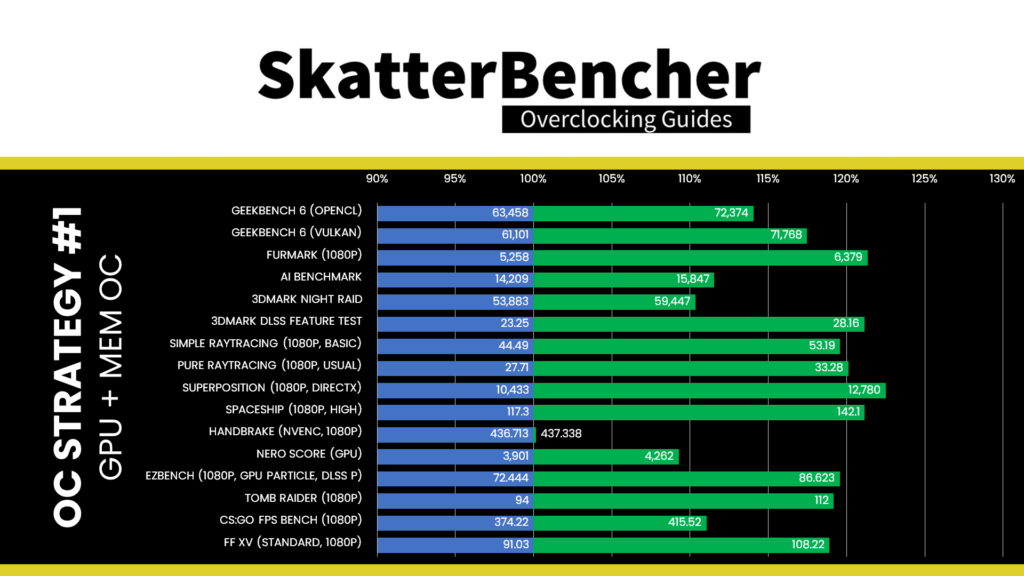
We re-run some benchmarks to ensure everything works as intended and check the performance increase compared to the default settings. With our RTX 3050 running 26% higher GPU frequency and 19% higher memory frequency, at 2235 and 2075 MHz, respectively, we see the highest performance in all benchmarks. The performance increase ranges from +0.14% in Handbrake to 22.50% in Unigine Superposition.
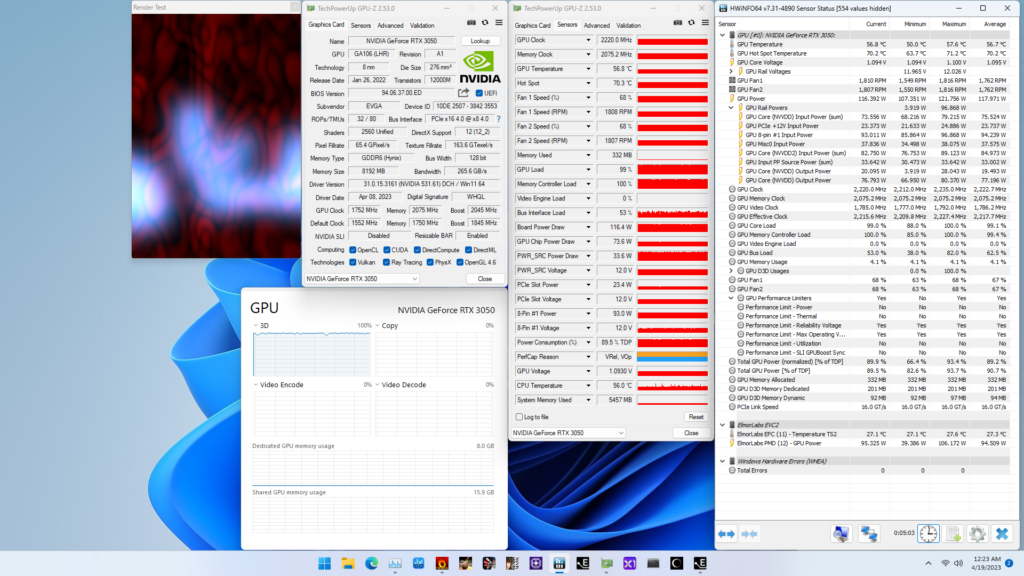
When running the GPU-Z Render Test, the maximum GPU Clock is 2235 MHz with 1.100V.
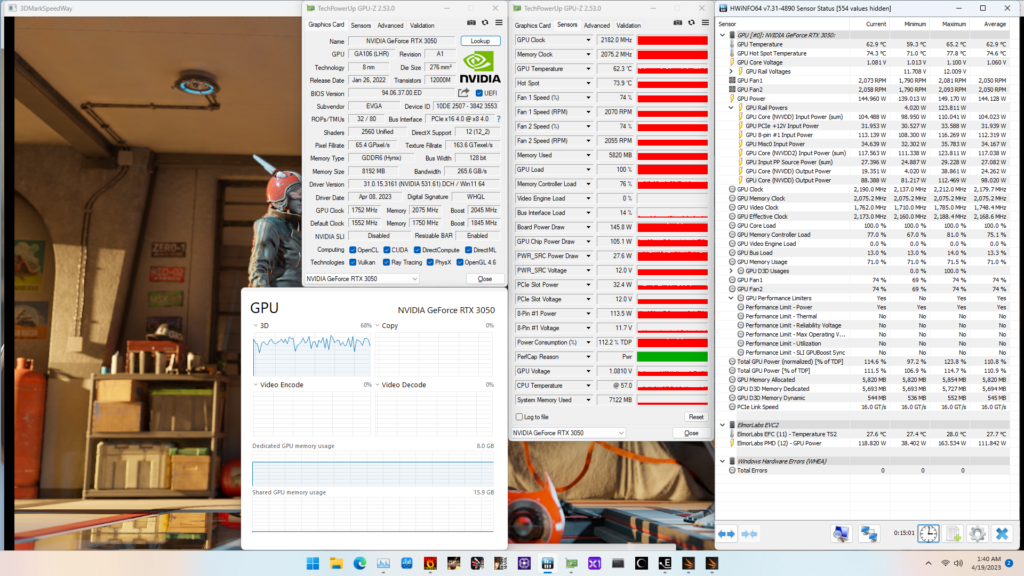
When running the 3DMark Speedway Stability Test, the average GPU effective clock is 2169 MHz with 1.060 volts, and the GPU Memory clock is 2075 MHz. The average GPU and GPU Hot Spot temperatures are 62.9 and 74.6 degrees Celsius. The average GPU power is 144.128 watts.
When running the Furmark GPU Stress Test, the average GPU effective clock is 1988 MHz with 0.907 volts, and the GPU Memory clock is 2075 MHz. The average GPU and GPU Hot Spot temperatures are 62.7 and 75.3 degrees Celsius. The average GPU power is 144.754 watts

And that’s it. I thank you for watching and the Patreons for the support. See you next time!
